Eth Labels
A public dataset of crypto addresses labeled (Ethereum and MANY more EVM chains)
A public API to consume this data is available for free. You can use it remotely here
Give your AI the ability to identify any crypto address. Works with Claude, Cursor, Windsurf, VS Code, and any MCP-compatible client.
170k+ labeled addresses and tokens across EVM chains.
Requires: Node.js 18+
npm install -g eth-labels-mcpThen use eth-labels-mcp as the command in your client config below (instead of the node /path/to/... approach).
git clone https://github.com/dawsbot/eth-labels.git
cd eth-labels/mcp
npm install
npm run buildAfter installing, add the server to your tool. Replace /absolute/path/to/eth-labels with where you cloned the repo.
Claude Code (one-liner)
claude mcp add eth-labels -- node /absolute/path/to/eth-labels/mcp/dist/index.jsThat's it. Claude Code handles the rest.
Claude Desktop
Edit your config file:
| OS | Path |
|---|---|
| macOS | ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json |
| Windows | %APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json |
| Linux | ~/.config/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json |
{
"mcpServers": {
"eth-labels": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["/absolute/path/to/eth-labels/mcp/dist/index.js"]
}
}
}Restart Claude Desktop after saving.
Cursor
Add to .cursor/mcp.json in your project root (or open Settings → Features → MCP Servers → Add):
{
"mcpServers": {
"eth-labels": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["/absolute/path/to/eth-labels/mcp/dist/index.js"]
}
}
}Windsurf
Add to ~/.codeium/windsurf/mcp_config.json:
{
"mcpServers": {
"eth-labels": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["/absolute/path/to/eth-labels/mcp/dist/index.js"]
}
}
}VS Code (GitHub Copilot)
Add to .vscode/settings.json in your project:
{
"mcp": {
"servers": {
"eth-labels": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["/absolute/path/to/eth-labels/mcp/dist/index.js"]
}
}
}
}Cline
Open Cline → MCP Servers → Configure, then add:
{
"mcpServers": {
"eth-labels": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["/absolute/path/to/eth-labels/mcp/dist/index.js"]
}
}
}💡 Tip: Always use absolute paths. Relative paths fail silently in most MCP clients.
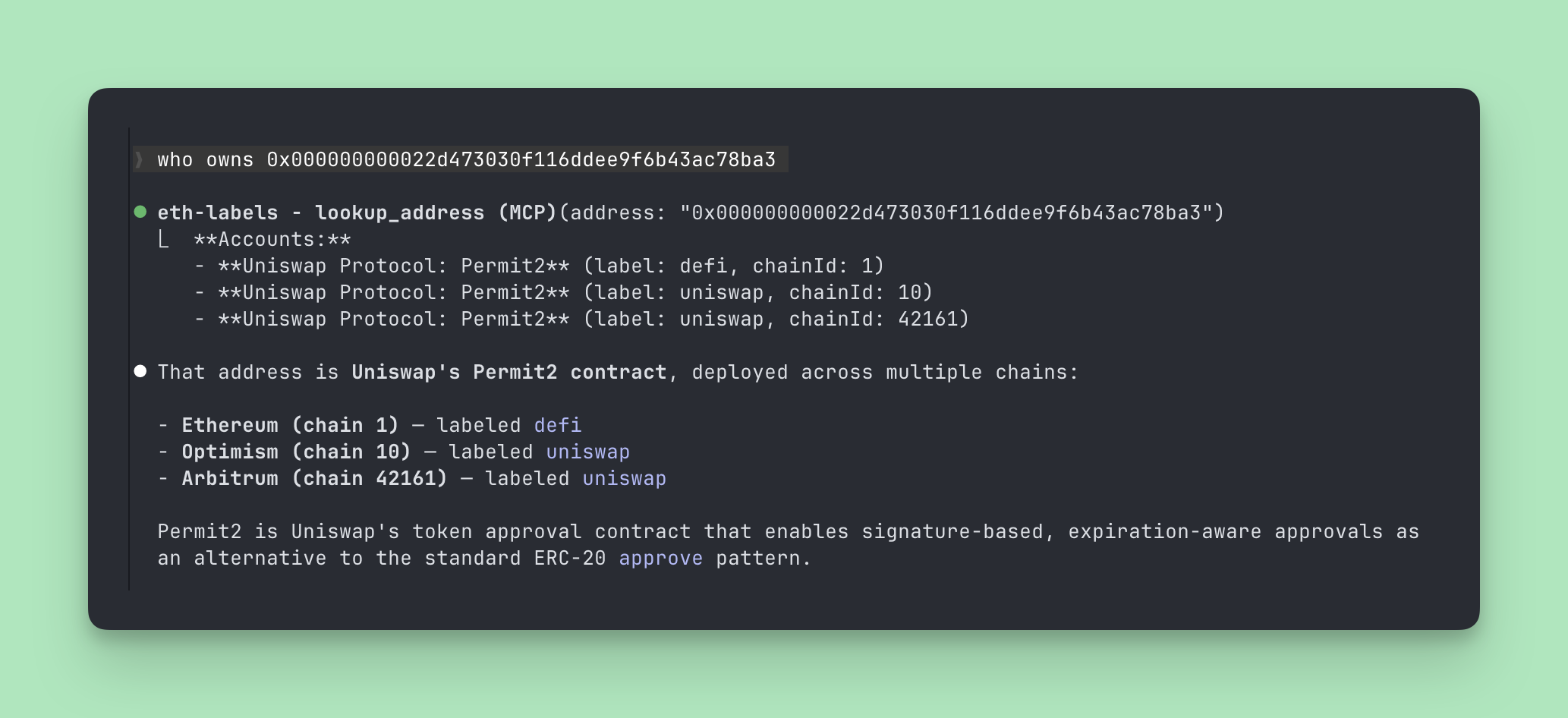
Once configured, ask your AI:
Who is 0xd8dA6BF26964aF9D7eEd9e03E53415D37aA96045?
If it responds with "Vitalik Buterin" — you're in.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
lookup_address |
Look up any Ethereum/EVM address to get its label and name tag |
search_labels |
Search by project name, label, or token symbol (e.g. "uniswap", "binance", "USDC") |
dataset_stats |
Get dataset statistics — 115k+ accounts, 54k+ tokens, 170k+ total entries |
Ask your AI: "Who owns 0xa6baaed2053058a3c8f11e0c7a9716304454b09e?"
- Where does this data come from?
- This data is already organized by the kind folks at Etherscan. Unfortunately that data is not accessible for researchers, so we've copied the data out and into a more shareable format here.
To use this API locally, start it like this:
bun run dev:apiDocumentation for the API is available via swagger at http://localhost:3000/swagger
This project includes an automated scraper that logs into Etherscan and pulls label data. No manual cookie copy-paste required!
- Create a
.envfile in the project root (see.env.example):
ETHERSCAN_USERNAME=your_etherscan_username
ETHERSCAN_PASSWORD=your_etherscan_password- Start Chrome with remote debugging (one of the following):
Option A: Clawdbot Managed Browser (recommended if you use Clawdbot)
- Clawdbot runs a managed Chrome instance at
ws://127.0.0.1:18800 - The scraper will automatically detect and use it
Option B: Manual Chrome with DevTools
# macOS
/Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome --remote-debugging-port=9222
# Linux
google-chrome --remote-debugging-port=9222Option C: Manual Cookie (fallback) If you can't run Chrome with remote debugging, you can manually extract cookies:
-
Log into Etherscan in your browser
-
Open DevTools → Application → Cookies → https://etherscan.io
-
Copy all cookies as a single string:
name1=value1; name2=value2; ... -
Add to
.env:ETHERSCAN_COOKIE=your_cookie_string_here -
Run the scraper:
bun run pullThe scraper uses Chrome DevTools Protocol (CDP) to connect to an already-running Chrome instance:
- Detects Chrome running at port 18800 (Clawdbot) or 9222 (standard DevTools)
- Connects via CDP (not launching a new browser — avoids Cloudflare automation detection!)
- Opens a new tab and navigates to etherscan.io/login
- Fills in credentials from environment variables
- Waits for you to solve the CAPTCHA (if present)
- Extracts cookies using CDP (including httpOnly cookies)
- Closes only the login tab (browser stays running)
- Uses those cookies for all subsequent requests
Why CDP? Connecting to a real Chrome instance avoids Cloudflare's automation detection. Unlike Puppeteer's launch(), which gets blocked, connecting to an existing browser looks like a normal browsing session.